Learning Targets
3.04A - I can identify the forces acting on an object/system, and draw a force diagram and/or system schema
Can You...
- Know forces (pushes and pulls) are interactions between two objects and be able to identify types of forces between objects by the way in which two objects interact.
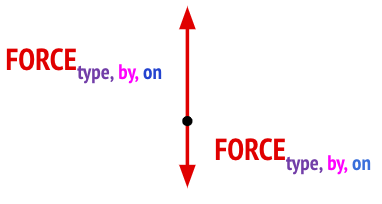
- Label forces, indicating the type of interaction between the objects, what object the force is acting on and what object the force is by. Use the following notation:
Fkind of force, by dealer, on feeler (For example: Fgravity by Earth on student)
- Know quantitatively, forces are measured in Newtons (pounds in the English system) and mass is measured in kilograms. A Newton is the same as a kilogram*meter/second/second. (N = kg*m/s/s )
A force is a push or pull upon an object resulting from the object's interaction with another object. Whenever there is an interaction between two objects, there is a force upon each of the objects. Forces only exist as a result of an interaction.
Types of Forces
Gravity |
Fg |
Attractive (toward each other) force between two objects with mass.
For objects on earth, the force of gravity acts between the object and the earth. This force is by definition the object’s weight and it acts on the object toward the center of the earth. |
Friction |
Ff |
Resistive force between two surfaces when surfaces they rub together. It opposes the motion of an object. For example, if a book slides across the surface of a desk, then the desk exerts a friction force in the opposite direction of its motion. Friction depends upon the type of each surface and how firmly they are pressed together.
|
Spring |
Fs |
Force exerted between compressed or stretched spring and an object attached to it.
The spring force acts toward restoring the spring to its unstretched or uncompressed length (equilibrium). Therefore, it acts opposite the direction of the stretch/compression. |
Normal |
FN |
Support force exerted between two surfaces that are in contact preventing them from passing through each other. Unlike friction, a normal force always acts perpendicular to (out of) the surface.
As an example, if a book is resting on the table, the table exerts an upward force on the book to support its weight and prevent it from falling. A normal force could also be exerted horizontally, for example when a person leans against a vertical wall. |
Applied |
Fg |
Force applied between an object and a person/object consciously and directly pushing/pulling it.
|
Tension |
FT |
Push or pull transmitted through a string, rope, cable, or wire, directed along the wire.
|
Electric |
FE |
Attractive or repulsive force between electrical charges.
|
Magnetic |
Fm |
Attractive or repulsive force between magnetic poles.
|
Buoyancy |
FB |
Force exerted between a fluid and an object immersed in the fluid. Pushes upward on the object.
|
Air Resistance |
FAir |
Special type of frictional force that acts upon between an object and the air it travels through, opposing the motion of the object.
|
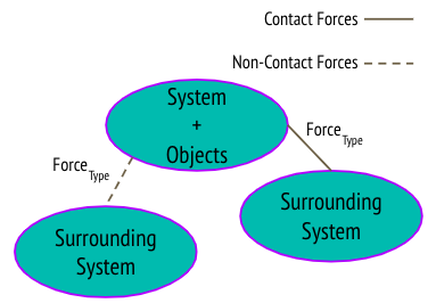
Systems
Most simply, a system is a group of objects.
A system is something we can decide, so choosing wisely is very important.
Internal forces are forces that only act between objects within the system
External forces are forces that act between an object in the system and an object outside the system.
A system is something we can decide, so choosing wisely is very important.
Internal forces are forces that only act between objects within the system
External forces are forces that act between an object in the system and an object outside the system.
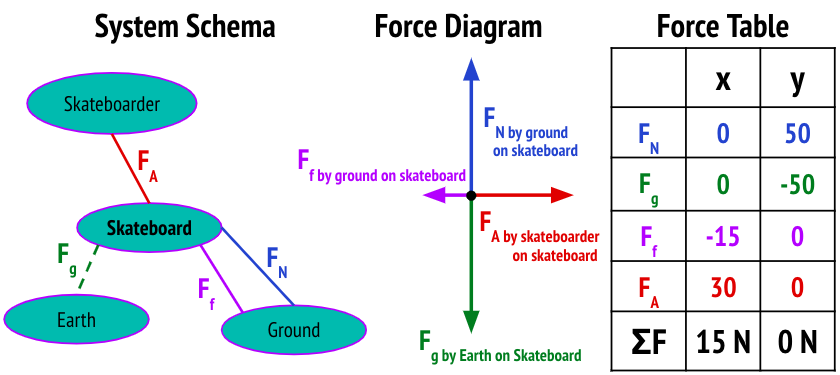
System Schemas
|
Force Diagrams
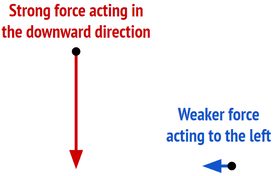
Forces are Vectors
|
Adding Vectors
|
Net Force
The net force [Fnet or ΣF] is the vector sum of all forces acting on an object.
|